♻️ Markets in a closed economy without State
The Goods and Services Market
The Composition of GDP
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is a measure of production over a certain period (usually a year or a quarter). It is noted
How is GDP computed? (Expenditure Approach):
- Consumption (
): Spending by households. - Investment (
): Spending by firms (capital). - Public Expenses (
): Spending by the State. - Net Exports (
): Exports minus Imports (Trade Balance).
In a closed economy without State,
Production Approach (Value Added)
To produce, firms need capital and labor. Value Added (VA) measures the wealth created by a productive unit. It is the difference between the value of production (Revenue) and the value of intermediate consumption (goods used up in the process).
Financial Markets
The Loanable Funds Market
Marchés des fonds traitables
Firms need money to invest. They find it on the Loanable Funds Market.
- Supply: Households who save money (Savings
). - Demand: Firms who want to invest (Investment
). - Price: The Interest Rate (
or ).
Money Neutrality
In the Neoclassical view, money is neutral. It is just a medium of exchange. The demand for money depends on the level of transactions (which depends on GDP
Trust is essential for money to be accepted.
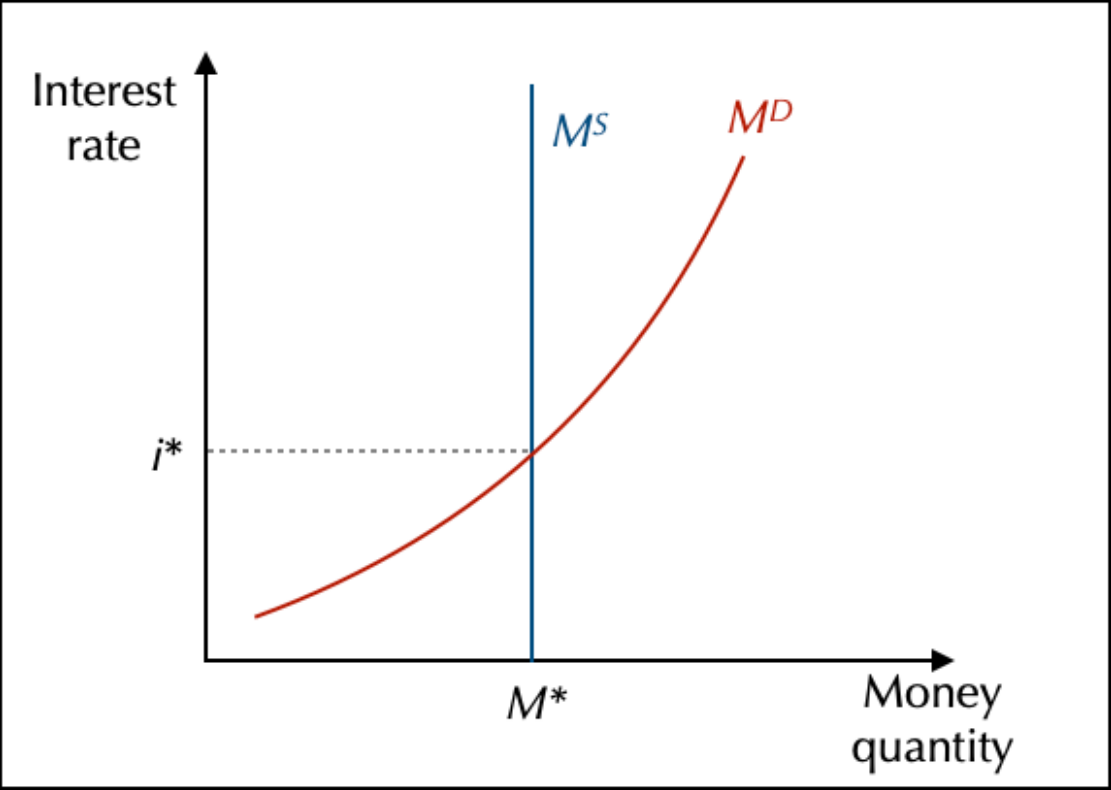
Money supply is exogenous, at a fixed supply. Salary can increase as same as prices, and so change nothing. So state interventions are useless (Say's Law).
Are cryptocurrencies going to replace money?
Inflation make money not trustable. Crypto isn't a currency, it's an asset. It's only created by mining.
To have a currency, you need 3 main options :
- Store of value :
- Accounting unit : price are defended and stables
- Medium of exchange : you need to be able to use it
So maybe, but they will be not our actual crypto which would be real currencies and not assets.
The labour market
Real wage and the construction of supply and demand on the labour market
Labor or Labour, both fine
Most of what is happening is depending of what workers want. In the neoclassical theory, workers are a pillar. They are seeking purchasing power coming directly on salary & prices (
The equilibrium on the market and its implications
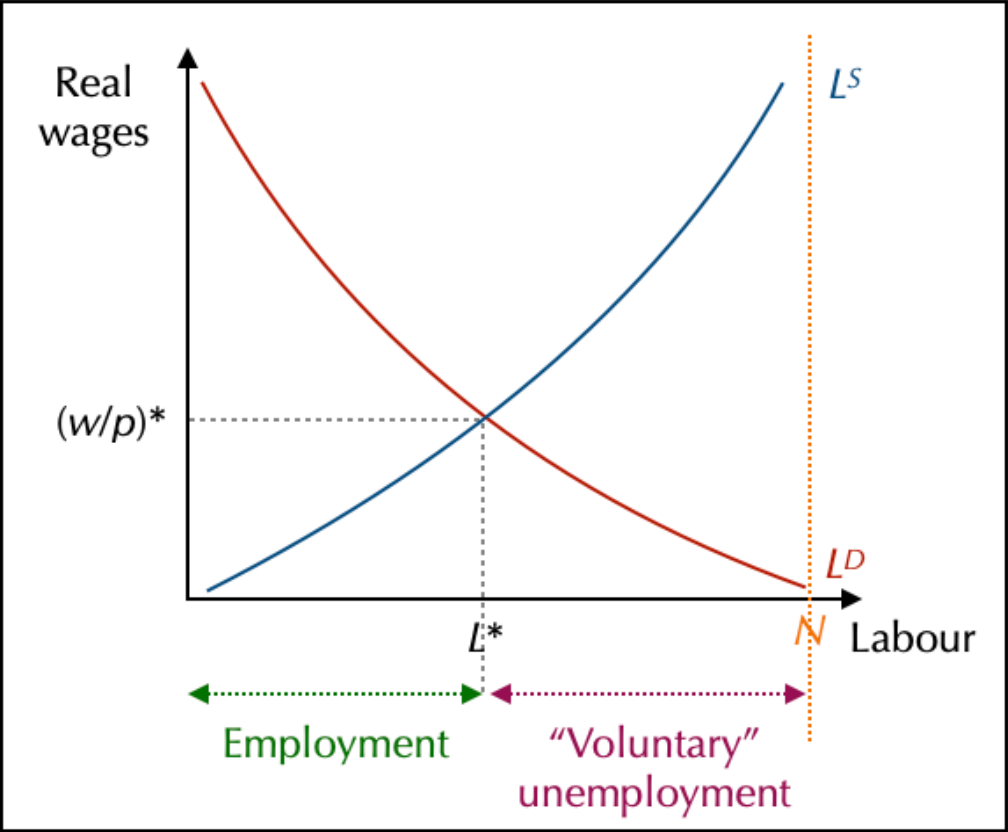
This shows that, for neoclassical, unemployment is voluntary.
